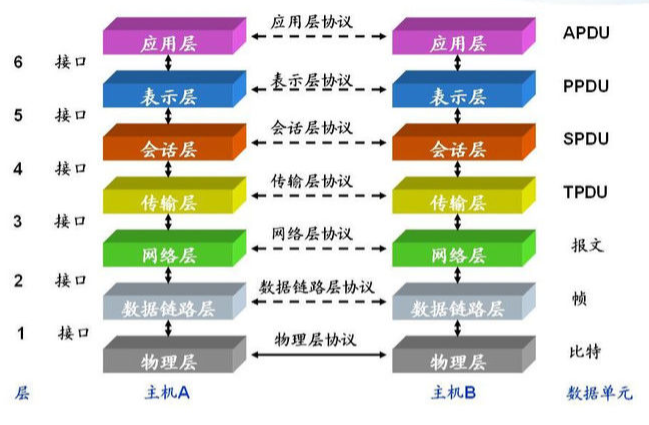
1. HTTP、TCP/IP、Socket
- HTTP 协议:超文本传输协议,对应于应用层,用于如何封装数据.
- TCP/UDP 协议:传输控制协议,对应于传输层,主要解决数据在网络中的传输。
- IP 协议:对应于网络层,同样解决数据在网络中的传输。
- Socket 是对TCP/IP协议的封装,Socket只是个接口(有create、listen、connect、accept、send、read和write等基础的函数提供),不是协议,通过Socket才能使用 TCP/IP 协议,除了 TCP,也可以使用 UDP 协议来传递数据
- RPC(Remote Procedure Call)—远程过程调用,建立在 tcp 协议基础上,比 http 更轻量、更快速。
2. Protocol Buffers
Protocol Buffers是google开源的一种结构数据序列化机制,可跨语言、跨平台。
相比XML、JSON、Thrift等其他序列化格式,Protocol Buffers的序列化和反序列化性能是很高的,且Protocol Buffers序列化后是二进制流,因此数据大小和传输速度是很好的。
1. 消息(message)定义
//定义一个message类型
message TestResponse {
// 定义TestResponse的成员变量,需要指定:变量类型、变量名、变量Tag
string name = 1;
int32 age = 2;
int32 height = 3;
}
使用message关键字,定义一个message后,会被不同语言编译成相应的对象,比如Go语言的struct、Java语言的class。
message内的字段一般包含:数据类型、字段名、字段编号tag
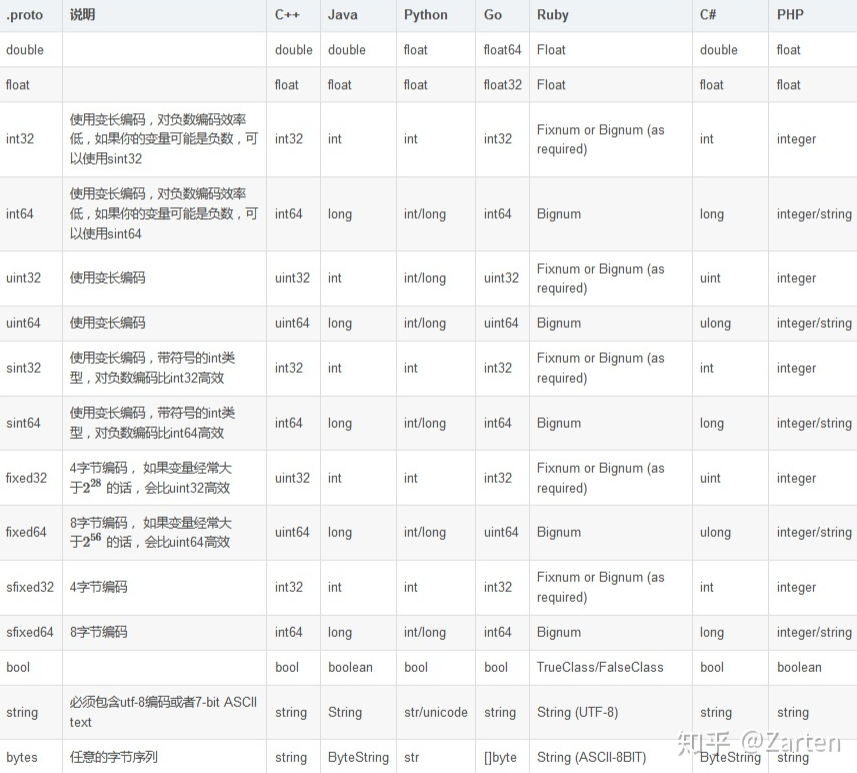
2. 数据类型
-
标量类型
-
复合类型
- 枚举
定义一个枚举可以在message的外部或内部定义,且第一个枚举值必须是0,每个枚举值不能重复,若必须要重复,可以使用option allow_alias = true来启用重复。定义枚举后可在proto文件中任意message中使用。
```proto enum ETest { option allow_alias = true; //开启枚举值重复开关 Test1 = 0; Test2 = 1; Test3 = 2; Test4 = 2; //开启option allow_alias = true后枚举值可以重复 }
//定义一个message类型 message TestOne { string name = 1; int32 age = 2; int32 height = 3; ETest eTest = 4; }
- 嵌套其他message
```proto
//定义一个message类型
message MoreTestResponse {
TestResponse test = 1; //使用其他message类型
int32 weight = 2;
}
//定义一个message类型
message TestResponse {
string name = 1;
int32 age = 2;
int32 height = 3;
}
- Map使用
map<key_type, value_type> map_field = N;
key_type:类型必须是字符串类型或整形。
value_type:可以是任意类型。
Map 是无序的
如果有相同的键会导致解析失败//定义一个message类型 message MoreTestResponse { string name = 1; int32 age = 2; map<int32,string> test = 3; //使用map }
- 字段名
- 修饰符
singular(默认):此字段在message中有0个或1个。
repeated:此字段在message中可以重复任意次数(类似数组),且会保留重复值的顺序。//定义一个message类型 message TestResponse { repeated string all_name = 1; //用repeated修饰,类似数组 } - 字段编号tag
编号tag就是“=”后面的数字1、2、3。每个字段在message内都需要定义一个唯一的编号tag,编号tag作用在于在二进制格式中唯一编码,所以编号tag一旦使用就不应再修改,且更新proto也不能修改,否则对旧版本无法兼容等问题出现。
编号tag的取值范围为[1, 2^29 -1] ,但 19000~19999 是 protobuf 预留的,用户不能使用。
不同范围的tag编码方式不同:
1 ~ 15:单字节编码
16 ~ 2047:双字节编码
因此使用频率高的编号tag最好设置成1~15,这样可以减小编码后的数据大小。 - reserved
若某些字段要删除或注释掉(凡是需要改变编号tag的操作),或需要预留一些编号tag,可以使用reserved来标注,用reserved标注后的tag再使用编译的时候直接报错,这样可以避免再次使用带来的各种风险。
reserved可以用来预留字段名和字段编号tag,可以用to来标识tag范围//定义一个message类型 message TestResponse { reserved 4, 6, 8 to 15; reserved "test1", "test2"; string name = 1; int32 age = 2; int32 height = 3; }
3. 定义service
- 简单rpc: 跟普通的函数调用一样,客户端发送请求,等待服务器端返回。
- 服务器端流式rpc: 客户端发送一个请求,服务器端收到请求后流式返回信息,客户端读取返回的流信息直到没有任何信息返回。在响应类型前用stream关键字修饰
- 客户端流式rpc: 客户端流式发送信息到服务器,在发送结束后等待服务器返回一个响应。在请求类型前用stream关键字修饰
- 双向流式rpc: 客户端和服务端双方都使用流发送信息,两个流独立操作。在请求类型和响应类型前用stream关键字修饰。
// 简单rpc
service TestServ {
//定义一个方法,接收一个TestRequest,返回一个TestResponse
rpc GetTestInfo (TestRequest) returns (TestResponse);
}
// 服务器端流式rpc
service TestServ {
//定义一个方法,接收一个TestRequest,返回一个TestResponse
rpc GetTestInfo (TestRequest) returns (stream TestResponse);
}
// 客户端流式rpc
service TestServ {
//定义一个方法,接收一个TestRequest,返回一个TestResponse
rpc GetTestInfo (stream TestRequest) returns (TestResponse);
}
// 双向流式rpc
service TestServ {
//定义一个方法,接收一个TestRequest,返回一个TestResponse
rpc GetTestInfo (stream TestRequest) returns (stream TestResponse);
}
4. Package
使用package可以避免命名冲突。
syntax = "proto3"; // 指定使用proto3,如果不指定的话,编译器会使用proto2去编译
package testpkg; //定义一个包
//定义一个message类型
message TestRequest {
// 定义TestRequests的成员变量,需要指定:变量类型、变量名、变量Tag
string id = 1;
}
5. 引用其他proto文件
使用import关键字进行引用
syntax = "proto3"; // 指定使用proto3,如果不指定的话,编译器会使用proto2去编译
import "test1.proto";
import public "test2.proto";
在文件A中两者可以直接引用它们上一级proto文件B的内容。不同的是,若文件B内使用了import引用文件C,则文件A不能使用文件C的内容;若文件B内使用了import public引用文件C,则文件A可以使用文件C的内容
3. gRPC
gRPC is a modern, open source, high-performance remote procedure call (RPC) framework that can run anywhere. gRPC enables client and server applications to communicate transparently, and simplifies the building of connected systems.
1. 定义proto文件
syntax = "proto3";
option java_multiple_files = true;
option java_package = "test.grpc_server.examples.helloworld";
option java_outer_classname = "HelloWorldProto";
package helloworld;
// The greeting service definition.
service Greeter {
// Sends a greeting
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
rpc testStream (HelloRequest) returns (stream HelloReply) {}
}
// The request message containing the user's name.
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
// The response message containing the greetings
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}
2. Java server
- POM文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>test</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc_server</artifactId>
<version>0.1.0</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<grpc.version>1.42.0</grpc.version><!-- CURRENT_GRPC_VERSION -->
<protobuf.version>3.17.2</protobuf.version>
<protoc.version>3.17.2</protoc.version>
<!-- <!– required for jdk9 –>-->
<!-- <maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source>-->
<!-- <maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target>-->
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-bom</artifactId>
<version>${grpc.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-netty-shaded</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-protobuf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-stub</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- <dependency>-->
<!-- <groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId>-->
<!-- <artifactId>protobuf-java-util</artifactId>-->
<!-- <version>${protobuf.version}</version>-->
<!-- </dependency>-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat</groupId>
<artifactId>annotations-api</artifactId>
<version>6.0.53</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- <dependency>-->
<!-- <groupId>io.grpc</groupId>-->
<!-- <artifactId>grpc-testing</artifactId>-->
<!-- <scope>test</scope>-->
<!-- </dependency>-->
<!-- <dependency>-->
<!-- <groupId>junit</groupId>-->
<!-- <artifactId>junit</artifactId>-->
<!-- <version>4.12</version>-->
<!-- <scope>test</scope>-->
<!-- </dependency>-->
<!-- <dependency>-->
<!-- <groupId>org.mockito</groupId>-->
<!-- <artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>-->
<!-- <version>3.4.0</version>-->
<!-- <scope>test</scope>-->
<!-- </dependency>-->
</dependencies>
<build>
<extensions>
<extension>
<groupId>kr.motd.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>os-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.6.2</version>
</extension>
</extensions>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.xolstice.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.6.1</version>
<configuration>
<protocArtifact>com.google.protobuf:protoc:${protoc.version}:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</protocArtifact>
<pluginId>grpc-java</pluginId>
<pluginArtifact>io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:${grpc.version}:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</pluginArtifact>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
<goal>compile-custom</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-enforcer-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>enforce</id>
<goals>
<goal>enforce</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<rules>
<requireUpperBoundDeps/>
</rules>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>6</source>
<target>6</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
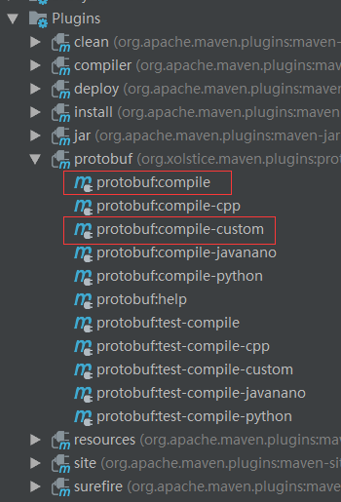
- 生成Java代码根据proto文件
proto文件需放在proj/src/main/proto文件夹下面
protobuf:compile生成的5个文件是与protobuf序列化相关的,也就相当于是数据交换时的java bean。
protobuf:compile-custom生成的1个文件是与grpc相关的,主要用于与服务端通信的。
- 实现service方法
package test.grpc_server.examples;
import io.grpc.stub.StreamObserver;
import test.grpc_server.examples.helloworld.GreeterGrpc;
import test.grpc_server.examples.helloworld.HelloReply;
import test.grpc_server.examples.helloworld.HelloRequest;
public class GreeterImpl extends GreeterGrpc.GreeterImplBase {
@Override
public void sayHello(HelloRequest req, StreamObserver<HelloReply> responseObserver) {
System.out.println("Get the client message::" + req.getName());
HelloReply reply = HelloReply.newBuilder().setMessage("Hello " + req.getName()).build();
responseObserver.onNext(reply);
responseObserver.onCompleted();
}
@Override
public void testStream(HelloRequest request, StreamObserver<HelloReply> responseObserver) {
System.out.println("Get the client message::" + request.getName());
responseObserver.onNext(HelloReply.newBuilder().setMessage("test 1").build());
responseObserver.onNext(HelloReply.newBuilder().setMessage("test 2").build());
responseObserver.onNext(HelloReply.newBuilder().setMessage("test 3").build());
responseObserver.onNext(HelloReply.newBuilder().setMessage("test 4").build());
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
responseObserver.onNext(HelloReply.newBuilder().setMessage("test 5").build());
responseObserver.onCompleted();
}
}
- 开启server
package test.grpc_server.examples;
import io.grpc.Server;
import io.grpc.ServerBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* Server that manages startup/shutdown of a {@code Greeter} server.
*/
public class HelloWorldServer {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(HelloWorldServer.class.getName());
private Server server;
private void start() throws IOException {
/* The port on which the server should run */
int port = 50051;
server = ServerBuilder.forPort(port)
.addService(new GreeterImpl())
.build()
.start();
logger.info("Server started, listening on " + port);
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
// Use stderr here since the logger may have been reset by its JVM shutdown hook.
System.err.println("*** shutting down gRPC server since JVM is shutting down");
try {
HelloWorldServer.this.stop();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(System.err);
}
System.err.println("*** server shut down");
}
});
}
private void stop() throws InterruptedException {
if (server != null) {
server.shutdown().awaitTermination(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
/**
* Await termination on the main thread since the grpc library uses daemon threads.
*/
private void blockUntilShutdown() throws InterruptedException {
if (server != null) {
server.awaitTermination();
}
}
/**
* Main launches the server from the command line.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
final HelloWorldServer server = new HelloWorldServer();
server.start();
server.blockUntilShutdown();
}
}
3. Typescript client
-
添加依赖
npm i @grpc/grpc-js @grpc/proto-loader google-protobuf -
动态代码生成
```typescript import * as grpc from ‘@grpc/grpc-js’ import * as protoLoader from ‘@grpc/proto-loader’
const PROTO_FILE_PATH = __dirname + ‘/../../grpc/proto/helloworld.proto’
export function getDynamicGrpcClient() {
const packageDefinition = protoLoader.loadSync(PROTO_FILE_PATH,
{
keepCase: true,
longs: String,
enums: String,
defaults: true,
oneofs: true
});
const hello_proto: any = grpc.loadPackageDefinition(packageDefinition).helloworld;
let client = new hello_proto.Greeter('localhost:50051', grpc.credentials.createInsecure())
client.SayHello({ name: "dynamic grpc" }, (err: any, response: any) => {
let module = JSON.parse(response.message);
console.log('Test grpc server:' + module)
interModule(module);
})
// 流方法
let call = client.testStream({ name: 'test stream' });
call.on('data', function (response:any) {
console.log('Test grpc stream:' + response.message);
});
call.on('end', function () {
console.log('Get all stream test infos ');
});
client.close() } ```
- 静态代码生成
- 生成ts代码 ```shell // windows OS npm i -g grpc-tools grpc_tools_node_protoc_ts mkdir gen-ts
// the plugin must be absolute path on win64 OS grpc_tools_node_protoc –plugin=protoc-gen-ts=C:/Users//AppData/Roaming/npm/protoc-gen-ts.cmd –ts_out=grpc_js:./gen-ts –js_out=import_style=commonjs:./gen-ts –grpc_out=grpc_js:./gen-ts -I ./proto ./proto/.proto
// linux OS // –unsafe-perm needed in docker npm install -g –unsafe-perm grpc-tools npm install grpc_tools_node_protoc_ts –save-dev
mkdir gen-ts
grpc_tools_node_protoc
–plugin=protoc-gen-ts=./../node_modules/.bin/protoc-gen-ts
–ts_out=grpc_js:./gen-ts
–js_out=import_style=commonjs:./gen-ts
–grpc_out=grpc_js:./gen-ts
-I ./proto
./proto/*.proto
会生成四个文件:helloworld_pb.js,helloworld_pb.d.ts,helloworld_grpc_pb.js,helloworld_grpc_pb.d.ts
- 创建client
```typescript
import * as grpc from '@grpc/grpc-js'
import * as protoLoader from '@grpc/proto-loader'
import { GreeterClient } from '../../grpc/gen-ts/helloworld_grpc_pb';
import { HelloRequest } from '../../grpc/gen-ts/helloworld_pb';
export function getStaticGrpcClient() {
const client = new GreeterClient(
"localhost:50051",
grpc.credentials.createInsecure()
);
const request = new HelloRequest();
request.setName("static way");
client.sayHello(request, (error, response) => {
if (!error) {
console.info("Test grpc server::", response.getMessage());
} else {
console.error("Error:", error.message);
}
});
const streamReq = new HelloRequest();
streamReq.setName('test stream');
let call = client.testStream(streamReq);
call.on('data', function (chunk) {
console.log('Test grpc stream:' + chunk.array[0]);
});
call.on('end', function () {
console.log('Get all stream test infos ');
});
client.close();
}
4. Thrift
Apache Thrift
Thrift
Thrift–实现NodeJS和Java间通信
由浅入深了解Thrift(一)——Thrift介绍与用法
Thrift demo
Apache Thrift系列详解(一) - 概述与入门
在nodejs使用typescript呼叫thrift client
5. HTTP + RESTful API
REST (REpresentation State Transfer) 描述了一个架构样式的网络系统,比如 web 应用程序。REST 指的是一组架构约束条件和原则。满足这些约束条件和原则的应用程序或设计就是 RESTful。
Restful 特点包括:
- 每一个URI代表1种资源;
- 客户端使用GET、POST、PUT、DELETE4个表示操作方式的动词对服务端资源进行操作:GET用来获取资源,POST用来新建资源(也可以用于更新资源),PUT用来更新资源,DELETE用来删除资源;
- 通过操作资源的表现形式来操作资源;
- 资源的表现形式是XML或者HTML;
- 客户端与服务端之间的交互在请求之间是无状态的,从客户端到服务端的每个请求都必须包含理解请求所必需的信息。
springboot-learning-example
Spring Boot 构建RESTful API
Node.js http请求java后台数据接口方法总结
浅析nodejs的http模块
6. Dubbo
apache dubbo
Your First Dubbo Demo
dubbo-samples
dubbo-js
dubbo quick starttt
Dubbo入门—搭建一个最简单的Demo框架
Node调用Java的示例代码(hessian)
Node.js通过Dubbo2.js调用Java
7. node-java
node-java
实战系列之 Node.js 玩转 Java
Protocol Buffers
Protocol Buffers3详解
gRPC的stream使用
gRPC
gRPC quick start(java)
Java:gRPC使用简介
gRPC(nodejs)
Nodejs使用gRPC与Java进行远程通信
gRPC Server and Client examples with Typescript
How to Effectively use GRPC Streams in NodeJS
Cannot find name ‘XMLHttpRequest’